Demystifying Hashgraph: The Future of Distributed Ledger Technology
Hashgraph
is a revolutionary distributed ledger technology (DLT) that offers several
unique features, promising to reshape the future of decentralized systems.
Developed by Swirlds, it employs a novel consensus algorithm to achieve
consensus and maintain the integrity of transactions across a network. At its
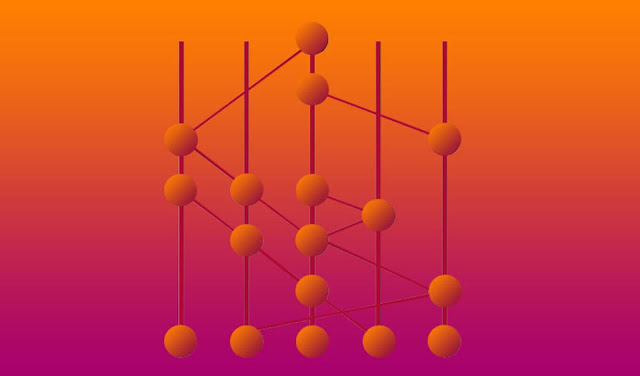
core, it utilizes a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure, where every
transaction is linked to one another through cryptographic hashes, forming a
graph-like structure. Unlike traditional blockchain systems, it does not rely
on miners to validate transactions. Instead, it utilizes a consensus algorithm
called "Gossip about Gossip" and "Virtual Voting" to
achieve agreement among network nodes.
In
the Gossip about Gossip mechanism, nodes exchange information about
transactions and their respective timestamps through a peer-to-peer
communication protocol. This ensures that each node is aware of the
transactions in the network, promoting transparency and efficiency. The Virtual
Voting mechanism is used to determine the order of transactions and reach
consensus on the state of the ledger. Nodes can vote on which transaction they
received first and share this information with other nodes. Through this
process, a consensus timestamp is established for each transaction, forming a
chronological order of events.
The key benefits of Hashgraph include:
1. Speed
and Scalability: It can process thousands of transactions per second,
significantly outperforming traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
This high throughput is crucial for real-world applications and mass adoption.
2.
Fairness and Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT): It achieves aBFT,
meaning it can tolerate malicious nodes without sacrificing consensus. It
guarantees fairness and security, even in the presence of faulty or malicious
actors.
3.
Low Transaction Fees: The absence of miners in it eliminates the need for
transaction fees typically associated with blockchains. This makes
microtransactions and low-value transactions economically viable.
4.
Reduced Energy Consumption: The lack of resource-intensive mining in Hashgraph
results in a greener and more energy-efficient network compared to traditional
proof-of-work blockchains.
5.
Security and Trust: Hashgraph's underlying consensus algorithm provides robust
security, ensuring that the system is resistant to attacks and manipulation.
However,
it also faces challenges, including intellectual property concerns due to its
patented algorithm and centralization concerns arising from its initial
closed-source approach. In conclusion, Hashgraph represents a promising advancement in distributed ledger
technology, offering a more efficient, scalable, and secure alternative to
traditional blockchains. Its potential to revolutionize various industries,
from finance to supply chain management, has garnered significant attention. As
the technology continues to evolve and its intellectual property barriers are
addressed, it may indeed shape the future of decentralized systems, providing a
foundation for innovative and trusted applications in the digital age.



Comments
Post a Comment